Brown Adipose Tissue
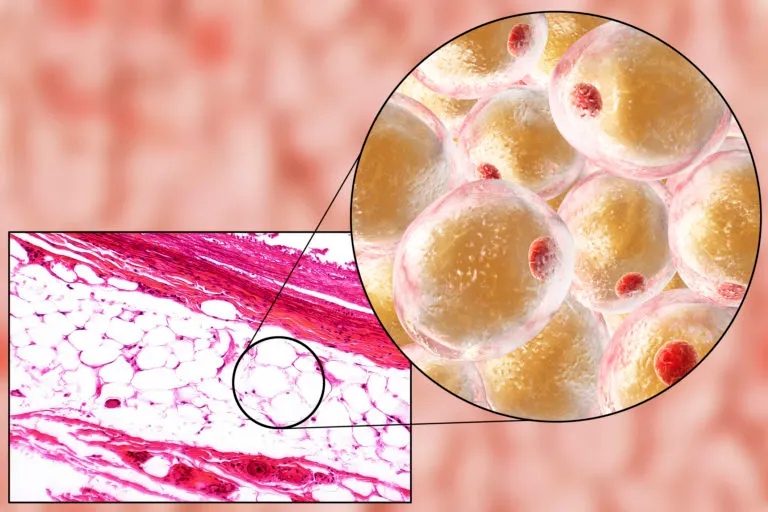
Adipose Brown Tissue and Weight Control.
What is Adipose Brown Tissue?
Brown fat cells are brown because they contain an enormous number of mitochondria, which are the power generators of cells,” says Sheila Collins, PhD, professor of the Integrative Metabolism Program at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute in Orlando, Florida. Within these mitochondria, brown fat cells burn fatty acids and glucose [sugar], producing heat. So rather than store fat as white fat cells do, brown fat cells burn calories while producing heat.
Weight loss advice often ignores the processes already happening in the body that support losing weight. Here’s a closer look at brown adipose tissue and how it can help the body shed pounds. The body has four main types of fat: white fat, brown fat, subcutaneous fat and visceral fat. Each type of fat has a different role; not all fats are bad. Fat cells are normally thought of as something that you don’t want a lot of. However, there is a type of fat called brown fat that may be beneficial for weight loss. In many ways, brown fat acts the opposite of traditional white fat cells.
As an infant, we naturally have brown fat, and it was thought that as we age, it goes away. Adults were thought to have very minimal if any, brown fat. Therefore, research has shown that if adults can increase their fat in brown stores, it may be helpful for weight loss. In 2007 study researchers found that adults do have varying amounts of brown adipose cells. Researchers are still trying to understand how brown fat is used in adults, how it could play a role in weight management and how/if it is possible to increase brown fat. When you think of losing fat, it is the fat white cells you are trying to lose. Most body fat adults have is considered white fat.
White fat cells store energy and burn very little energy. They can also release something called cytokines which are hormones that can interfere with various body functions. Carrying too much white fat, especially around body organs, can increase the risk for type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and other chronic diseases. On the other hand, brown fat cells are brown because they have more mitochondria. Mitochondria are considered powerhouses of cells because this is where nutrients are broken down and used for energy.
Brown fat tissue also has something called uncoupling protein-1 (UCP-1), which scientists believe helps increase metabolic rate. As fuels are being broken down for ATP, UCP can make this process somewhat inefficient, meaning more energy is needed to get fuel. Researchers are continuing to study the role UCP may have in fighting obesity (3). White fat – also known as white adipose tissue – stores energy and produces important hormones, such as adiponectin, which makes a person less likely to get diabetes or suffer from cardiovascular diseases. Subcutaneous fat is located just underneath the surface of the skin. This is one of the types of fats that accumulate when someone has more weight on them than they should.
A little subcutaneous fat is considered healthy to have as long as it’s not too much. Visceral fat is fat that accumulates around the organs and has a negative impact on health if there is too much of it surrounding vital organs. This type of fat is linked with everything from diabetes and cardiovascular disease to a higher risk of stroke. Brown fat – also known as brown adipose tissue – is the most interesting fat in terms of its direct links with weight loss. When brown fat is stimulated, it actually burns calories. It is brown fat that keeps you warm when it gets cold. The cold activates brown fat to produce warmth through a process called thermogenesis. As well as keeping you warm, thermogenesis helps break down too much of the other fats in the body, increasing metabolism.
Research shows that a higher amount of brown fat is found in slim people than it is in overweight people and is thought to help leaner people stay slim. Once an individual has more brown adipose tissue in their body, the effects of their weight loss regime should start to kick into effect. In particular, brown fat enables the body to burn calories all the time, not just when exercising. Furthermore, having more brown adipose tissue helps the body regulate its temperature better since one of the core purposes of this brown fat is thermogenesis. A body with a better-regulated temperature is one in which organs can function more optimally, keeping metabolism at a healthy rate. This also helps with weight loss before any exercise, or healthy eating is even done.
Another great benefit of having more brown fat in the body is that it helps to regulate both insulin and leptin levels. Insulin helps to maintain glucose levels, which can particularly help if someone is transitioning from unhealthy eating habits into healthier ones. Stable levels of leptin can also help to suppress appetite, so people don’t eat more than they need to.
Much of the research around brown adipose tissue also shows how people with more of it feel more energetic. Scientifically speaking, this is because it supports the breakdown of glucose into energy.have